Paris Summer Innovation Fellowship
I am participating in the 2016 Paris Summer Innovation Fellowship on the Data Science track with the project:
Optimizing restaurant health inspections through advanced analytics
The Ministry of Agriculture, Agri-food, and Forestry of France (Ministère de l’Agriculture, de l’Agroalimentaire et de la Forêt) regularly inspects businesses serving food to ensure restaurants and other food retail outlets are following safe food handling procedures. Such task is bounded by time and human resources, in other words, there is not enough time to inspect all restaurants in one year and there are not enough inspectors to speed up the process.
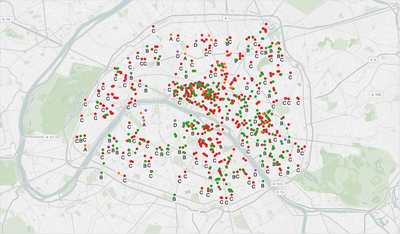
During 2015, 843 restaurants were inspected only in the Paris region. Each inspected restaurant was awarded a note:
A: Everything is correct, no issues found [Best] B: Correct with minor issues C: Major issues that need to be corrected D: Major issues were previously found and were not corrected [Worst]
Given this scenario, one way to optimize the use of resources for the restaurant health inspections is by focusing on those restaurants with higher risk. Since the number of inspectors is limited, a crowdsourcing solution was proposed using information available in platforms like TripAdvisor, where clients write ‘informal’ reviews of restaurants. The assumption is that informal reviews potentially contain hints of health issues. Given the popularity of services as TripAdvisor, the number of reviewed restaurants is considerably larger than the number of inspected restaurants. TripAdvisor contains reviews for 8x the number of restaurants inspected in 2015 in the Paris Region.
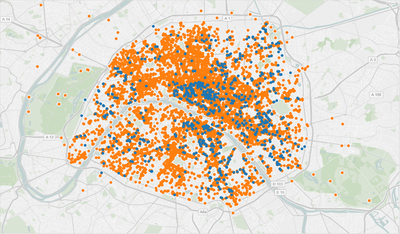
In the map, blue dots correspond to inspected restaurants (Ministry of Agriculture) and orange dots correspond to reviewed restaurants (TripAdvisor).
Predicting health risks from restaurant reviews

The project is composed of four major stages:
- Restaurants matching
Since the data sets of reviews and inspections were not created by the same entity we needed to merge them, in order to do so, two attributes were used: the
restaurant name and the address (franchise restaurants can have the same name but not the same address). The criteria used to match two restaurants was:
(fuzzy matching of the restaurant name is above 90)
AND(addresses are within the range of 100 meters) - Feature extraction Reviews were processed in order to find features (words) with high correlation to the task at hand (health issues). The top 60 words were extracted and used to generate boolean features along with statistical features such as variance, average number of reviews, etc.
- Supervised Learning The health risk prediction problem is an example of multi-label prediction, using the features extracted from the reviews and the health notes (A-D) from the inspections a supervised learning model was trained. We used tree based algorithms, namely Random Forest and Gradient Boosting. From test results, Gradient Boosting was selected as the best performer with cross-validated mean accuracy of 77.4%.
- Applying the prediction model Once the prediction model was trained, we applied it into the unlabeled data. In other words, the model predicted the health notes for those reviewed restaurants for which an inspection had not been performed.
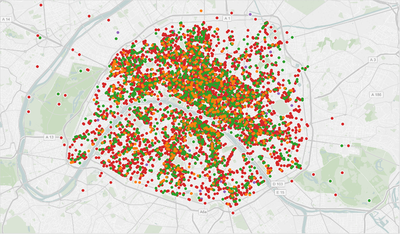
Model in action. The map shows the locations of the restaurants with reviews from TripAdvisor, colors correspond to the predicted health note (A-D).
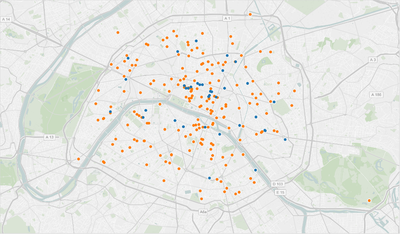
This map shows the locations of inspected restaurants with the lowest notes (D), blue dots correspond to inspected restaurants while orange dots correspond to the model predictions. The model was able to predict 3 times the number of potential high risk restaurants based on the user reviews. This way the Ministry of Agriculture can efficiently define where to allocate resources and what restaurants/regions should have higher priority.